Raw Material Handling
At Active Steel Forge, we recognize that the foundation of…
At Active Steel Forge, we recognize that the foundation of…
At Active Steel Forge, we offer advanced heating facilities designed…

Experience unmatched cutting precision and efficiency with our advanced cutting…
At Active Steel Forge, our advanced forging facilities offer unmatched…

At Active Steel Forge, we specialize in providing advanced heat…
Experience unmatched precision and superior quality with our advanced CNC…

7 min Read
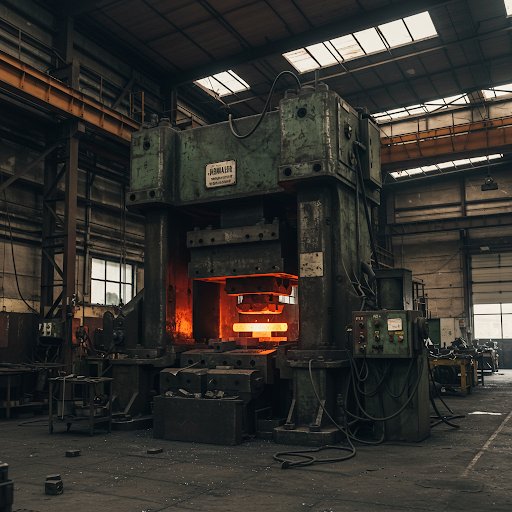
Steel forging, the art of shaping metal through the application of heat and pressure, has been a cornerstone of manufacturing for centuries. From the ancient blacksmiths who crafted tools and weapons to the modern industrial giants that produce components for aerospace and automotive industries, forging has played a pivotal role in human civilization. As technology advances, so too does the field of steel forging, with innovations driving the industry towards greater efficiency, precision, and sustainability.
As technology continues to advance, the field of steel forging is poised for continued innovation and growth. The integration of advanced technologies, the development of new materials, and a focus on sustainability will drive the industry towards a future of greater efficiency, precision, and environmental responsibility.
The future of steel forging is bright, with a focus on innovation, sustainability, and continuous improvement. By embracing these trends and leveraging the power of advanced technologies, the forging industry can continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of manufacturing and driving progress across a wide range of industries.
Get in touch with our experts today
