Raw Material Handling
At Active Steel Forge, we recognize that the foundation of…
At Active Steel Forge, we recognize that the foundation of…
At Active Steel Forge, we offer advanced heating facilities designed…

Experience unmatched cutting precision and efficiency with our advanced cutting…
At Active Steel Forge, our advanced forging facilities offer unmatched…

At Active Steel Forge, we specialize in providing advanced heat…
Experience unmatched precision and superior quality with our advanced CNC…

9 min Read
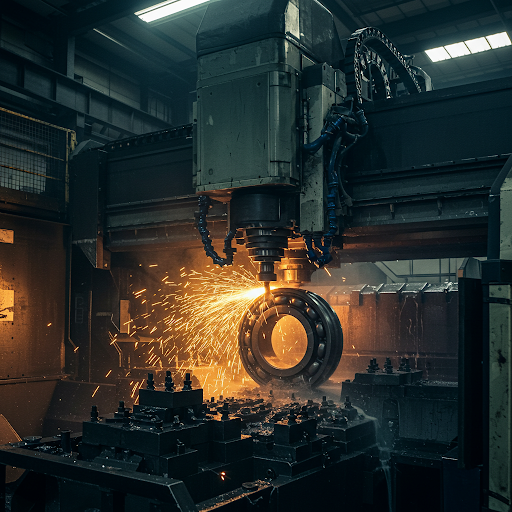
Heat treatment is a crucial process in forging that enhances the mechanical properties of metal components. By carefully controlling temperature, heating duration, and cooling rates, manufacturers can improve hardness, toughness, strength, and resistance to wear. This guide explores the different heat treatment processes in forging, their significance, and how they impact the overall quality of forged components.
Forging involves shaping metal through compressive forces, but to achieve optimal mechanical properties, heat treatment is essential. It alters the microstructure of the metal, refining grain structure and relieving internal stresses, which enhances durability and performance in demanding applications.
Annealing involves heating the forged metal to a specific temperature, holding it at that temperature, and then cooling it slowly. This process softens the metal, making it easier to machine and improving its ductility.
Normalizing is a process where metal is heated above its recrystallization temperature and then air-cooled. This treatment improves mechanical properties and refines the grain structure.
Quenching involves rapidly cooling the forged component by immersing it in water, oil, or air after heating. This process increases hardness and strength but can also make the material brittle.
Tempering follows quenching to reduce brittleness while maintaining the increased hardness and strength. It involves reheating the quenched material to a lower temperature, followed by controlled cooling.
Case hardening involves adding a hardened outer layer to a softer core. Carburizing introduces carbon into the surface, while nitriding introduces nitrogen to increase surface hardness.
The effectiveness of heat treatment depends on the material used. Different alloys respond uniquely to heat treatment, making material selection a crucial factor in achieving desired properties.
Heat treatment is essential in various industries where durability, strength, and wear resistance are critical.
To ensure consistency and reliability, manufacturers implement strict quality control measures in heat treatment processes.
Despite its benefits, heat treatment comes with challenges that manufacturers must address.
As technology advances, heat treatment processes continue to evolve, incorporating automation and innovative techniques.
Heat treatment plays a pivotal role in the forging industry, ensuring that components meet the highest standards of strength, durability, and reliability. By understanding the various heat treatment techniques, their benefits, and industry applications, manufacturers can optimize performance and quality in forged products. As advancements in metallurgy and automation continue, heat treatment processes will become even more efficient, contributing to innovation and excellence in precision manufacturing.
Whether you are selecting forged components for automotive, aerospace, or heavy machinery applications, partnering with an experienced manufacturer ensures that you receive high-quality, heat-treated products tailored to your industry’s specific needs.
Get in touch with our experts today
